Teachers pages now on Unisciences
New Embeded Timetables
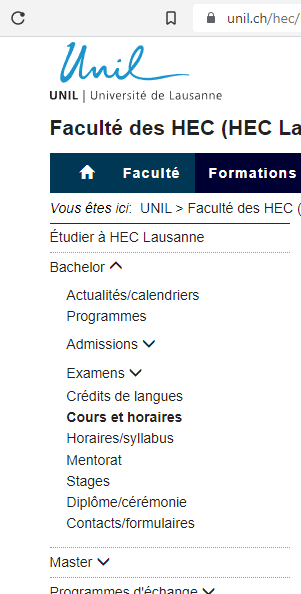
Please find Courses and timetables directly in your
Study program
Please find the Units charts now in Unisciences
Please find the Units charts now in Unisciences
![[logo_unil.png]](https://hecnet.unil.ch/medias/plone/lg14/logo_unil.png)